What is brain cavernoma and its causes?
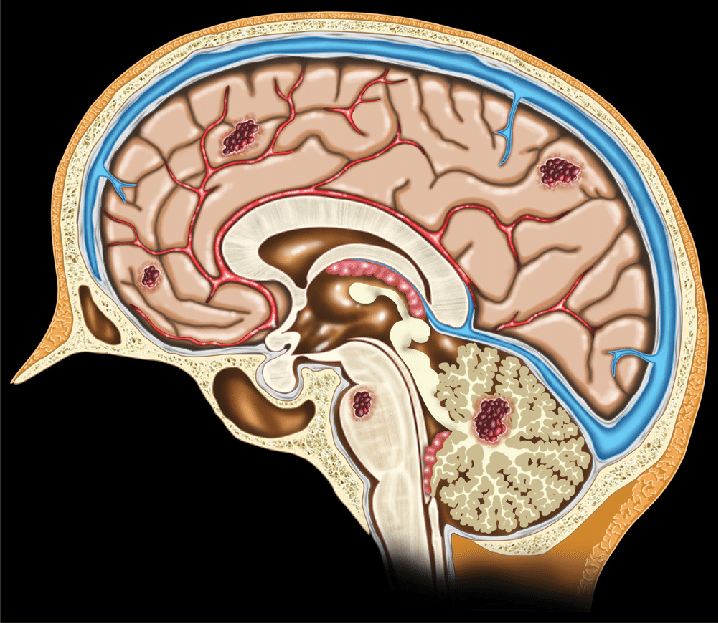
Cerebral cavernoma, also known as cavernous angiomas, is a vascular malformation that appears during brain development. The cavernoma evolves to cause problems in the brain and spinal cord, and its size can vary from 2 millimeters to several centimeters.
On the other hand, cavernomas may be single lesions, or there may be several malformations around different regions of the brain. Multiple carcinomatosis is the medical term for this condition.
Symptoms
Although the most common is to experience certain symptoms, such as those detailed below, they can also develop without presenting apparent symptoms.
The most common are:
- seizures
- Vision or focus problems.
- Weakness and tiredness.
- Intense headache.
- Difficulty speaking and understanding others.
However, the signs and symptoms should be evaluated by a specialist, and it is advisable to see a doctor if the patient presents:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Numbness on one side of the body.
- Sudden severe headache.
- Loss of vision or double vision.
- Difficulties with balance.
Causes
Although it responds to hereditary causes, cavernous cerebral malformations can also appear on their own. And to a lesser extent, cavernous malformations can appear after focal brain radiation therapy.
Diagnosis
There are different diagnostic methods for cerebral cavernoma. Nuclear magnetic resonance is the most used technique since it allows detection of hemosiderin with great sensitivity.
Only in some cases is magnetic resonance imaging used, and it is used, above all, to observe the possible multiple lesions of patients with cerebral cavernoma.
Treatment
The best treatment is prevention. For this, it is essential to regularly go to the doctor and carry out the pertinent check-ups. If the condition has already been detected, an MRI should be done every five years to track the progression of the cavernoma.
Surgical excision will be required whenever possible for those cases in which the lesion causes neurological deficits or cerebral hemorrhages.
What specialist treats you?
The neurosurgeon is the specialist in charge of cerebral cavernoma diagnosis and evaluation.